In the realm of data, a colossal force has emerged—Big Data Technology. Its immense volume, variety, velocity, and veracity hold the key to unlocking unprecedented insights, driving innovation, and transforming industries worldwide.
Big Data has shattered traditional data boundaries, opening up a new era of data-driven decision-making. From healthcare to finance, manufacturing to retail, Big Data is empowering organizations to optimize processes, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge.
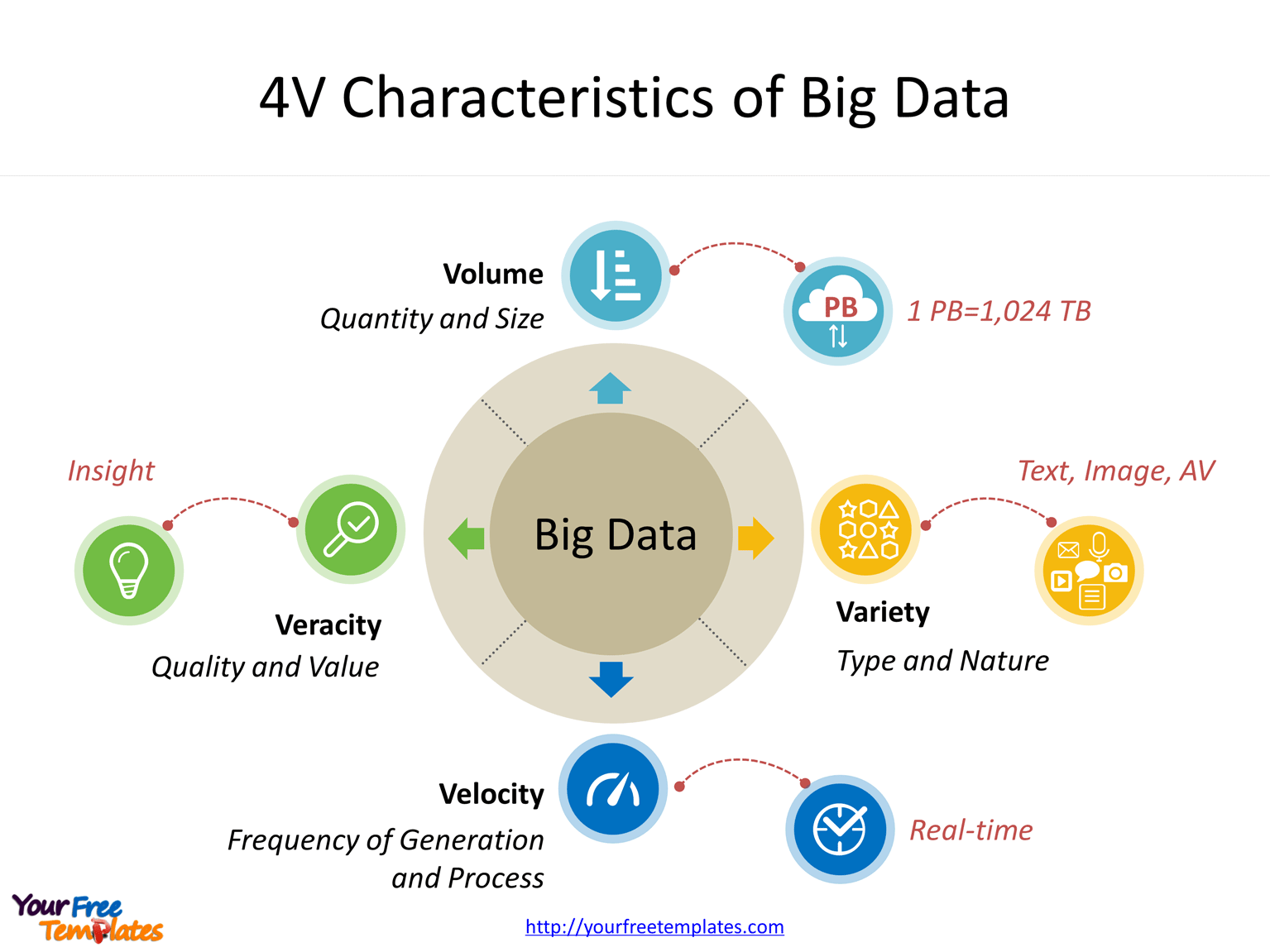
Big Data Definition and Characteristics
Big data refers to massive, complex datasets that are characterized by their volume, variety, velocity, and veracity. The sheer volume of data makes it challenging to process and analyze using traditional methods. The variety of data includes structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data, which poses challenges in data integration and analysis.
The velocity refers to the rapid generation and streaming of data, requiring real-time processing capabilities. Finally, veracity refers to the quality and accuracy of the data, which is crucial for making informed decisions.
Key Features and Attributes
Key features of big data include its ability to capture and analyze large volumes of data, handle diverse data types, and process data in real-time. It also enables organizations to identify patterns, trends, and insights from the data, leading to improved decision-making and operational efficiency.
Examples of Applications
Big data is utilized across various industries and applications. In healthcare, it is used for personalized medicine, disease diagnosis, and drug discovery. In finance, it is used for fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading. In retail, it is used for customer segmentation, targeted marketing, and inventory management.
Other applications include social media analysis, weather forecasting, and scientific research.
Big Data Technologies: Big Data Technology
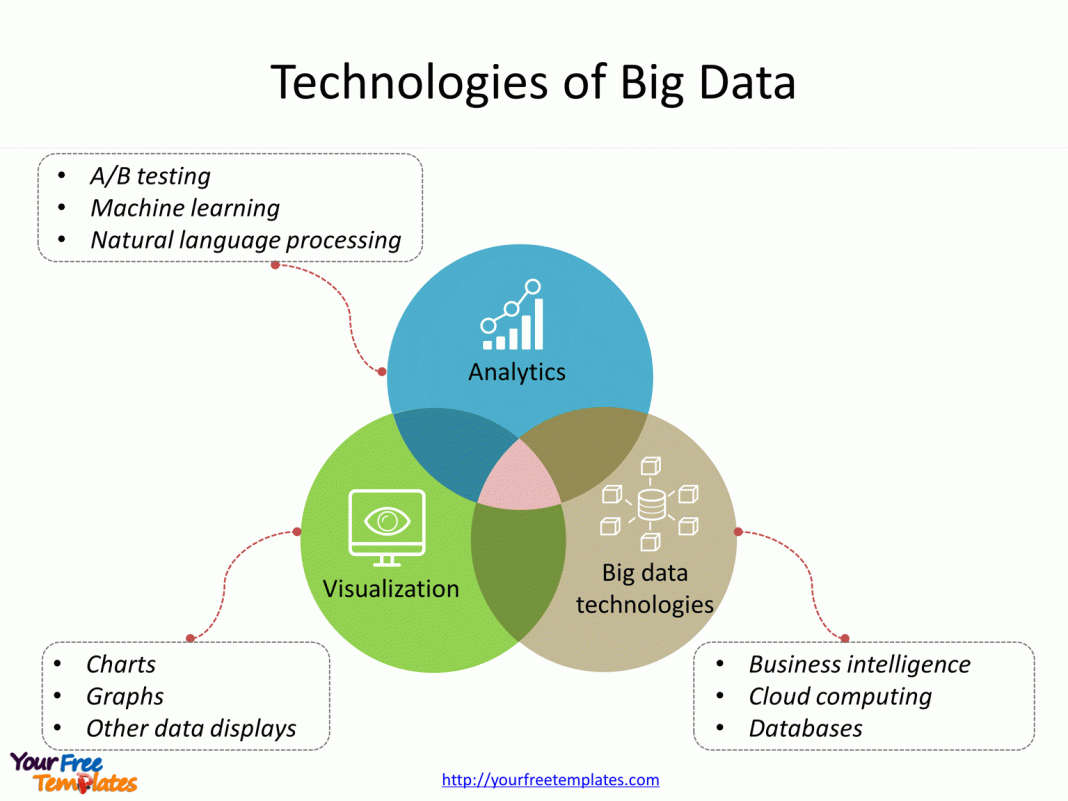
Big data technologies encompass a wide range of tools and frameworks designed to handle the challenges of processing and analyzing vast and complex datasets. These technologies provide the infrastructure and capabilities necessary to extract meaningful insights from big data.
Hadoop Ecosystem
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS):A distributed file system that stores data across multiple nodes, providing fault tolerance and scalability.
- MapReduce:A programming model for processing large datasets in parallel, distributing computations across multiple nodes.
- Apache Hive:A data warehouse system that enables querying and analyzing data stored in HDFS using SQL-like syntax.
- Apache Pig:A high-level data processing language that simplifies the development of complex data pipelines.
Apache Spark, Big data technology
A unified analytics engine that combines the capabilities of Hadoop MapReduce with in-memory computing, enabling faster processing and complex data analysis.
NoSQL Databases
- Document-oriented databases:Such as MongoDB and CouchDB, store data as JSON documents, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Key-value stores:Like Redis and Cassandra, store data as key-value pairs, offering high performance and scalability for read-intensive applications.
- Wide-column databases:Such as HBase and Cassandra, are designed for storing large amounts of structured data with flexible schema, suitable for time series data and analytics.
The choice of big data technologies depends on the specific requirements of the data processing task, such as data volume, processing speed, and data structure.
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics involves extracting insights from vast and complex data sets to improve decision-making. It encompasses various types and methodologies for analyzing big data.
Types of Big Data Analytics
- Descriptive Analytics:Summarizes historical data to provide insights into past events.
- Predictive Analytics:Uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends and outcomes.
- Prescriptive Analytics:Optimizes decision-making by recommending actions based on data analysis and simulations.
Methodologies and Techniques
Big data analysis employs various methodologies and techniques, including:
- Data mining:Uncovers patterns and relationships within data.
- Machine learning:Trains algorithms to learn from data and make predictions.
- Statistical analysis:Uses statistical methods to analyze data and draw inferences.
- Data visualization:Presents data in visual formats for easier interpretation.
Challenges and Opportunities
Extracting insights from big data presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Challenges:Data volume, variety, velocity, veracity, and value (the “5 Vs”).
- Opportunities:Enhanced decision-making, improved customer experiences, and innovative product development.
Big Data Applications
Big data has become an indispensable tool across a wide range of industries, empowering organizations to make informed decisions, streamline operations, and drive innovation. Its impact is particularly evident in the following sectors:
Retail
- Personalized recommendations based on customer behavior and preferences
- Optimized pricing and inventory management through demand forecasting
- Enhanced customer service and targeted marketing campaigns
Healthcare
- Early disease detection and personalized treatment plans
- Improved drug development and clinical research
- Streamlined healthcare operations and cost reduction
Finance
- Fraud detection and risk management
- Customized financial products and services
- Enhanced portfolio optimization and investment strategies
Transportation
- Optimized routing and traffic management
- Predictive maintenance and reduced downtime
- Improved passenger experience and safety
Manufacturing
- Quality control and defect detection
- Predictive maintenance and reduced downtime
- Optimized supply chain management and logistics
Benefits and Challenges
While big data adoption offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges:
Benefits
- Improved decision-making through data-driven insights
- Optimized processes and increased efficiency
- Innovation and competitive advantage
Challenges
- Data storage and management
- Data security and privacy concerns
- Skills gap and lack of expertise
Big Data Security and Privacy
The massive volume and variety of data in big data systems pose significant security and privacy risks. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious attacks can compromise sensitive information, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
To protect big data from these threats, organizations must implement robust security measures and adhere to best practices. Encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems are essential for safeguarding data from unauthorized access. Data masking and anonymization techniques can protect sensitive information while preserving its value for analytics.
Ethical and Legal Implications
The collection and analysis of big data raise ethical and legal concerns. Individuals have the right to privacy and control over their personal information. Organizations must obtain informed consent before collecting and using personal data and ensure its confidentiality and security.
Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, impose strict requirements on organizations handling personal data. These regulations require organizations to have clear privacy policies, provide individuals with access to their data, and enable them to request its correction or deletion.
Closing Notes

As we navigate the ever-evolving Big Data landscape, it’s crucial to embrace its transformative potential while addressing the associated challenges. By leveraging the right technologies, implementing robust security measures, and adhering to ethical guidelines, organizations can harness the power of Big Data to drive progress and shape the future of data-driven decision-making.
Query Resolution
What are the key characteristics of Big Data?
Volume, variety, velocity, and veracity.
What are the common challenges in Big Data analytics?
Data integration, data cleansing, and extracting meaningful insights.
What are the ethical implications of Big Data collection and analysis?
Privacy concerns, data security, and potential bias.
