Solar power grid prices stand as a pivotal topic in the realm of renewable energy, shaping the integration of solar power into the electrical grid. This in-depth exploration delves into the intricacies of pricing mechanisms, incentives, and challenges, providing a comprehensive understanding of this transformative technology.
The costs associated with integrating solar power into the grid, influenced by factors such as installation size and location, are meticulously examined. Additionally, the effectiveness of incentives and subsidies in driving solar power development is thoroughly analyzed.
Solar Power Grid Integration Costs
Integrating solar power into the electrical grid involves various costs associated with the physical infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and operational expenses. These costs vary depending on factors such as the scale of the solar installation, its geographical location, grid connection requirements, and the regulatory environment.
The major cost components of solar grid integration include:
Infrastructure Costs
- Solar panels:The cost of solar panels has declined significantly in recent years, but it still represents a substantial portion of the total investment. The cost of solar panels varies depending on the type of technology used, the efficiency of the panels, and the size of the installation.
- Mounting systems:Solar panels need to be mounted on a sturdy structure that can withstand wind and snow loads. The cost of mounting systems varies depending on the type of system used and the size of the installation.
- Inverters:Inverters convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is used by the electrical grid. The cost of inverters varies depending on the size and efficiency of the inverter.
- Electrical wiring and balance of system (BOS) components:Electrical wiring and other BOS components are needed to connect the solar panels to the grid. The cost of these components varies depending on the size and complexity of the installation.
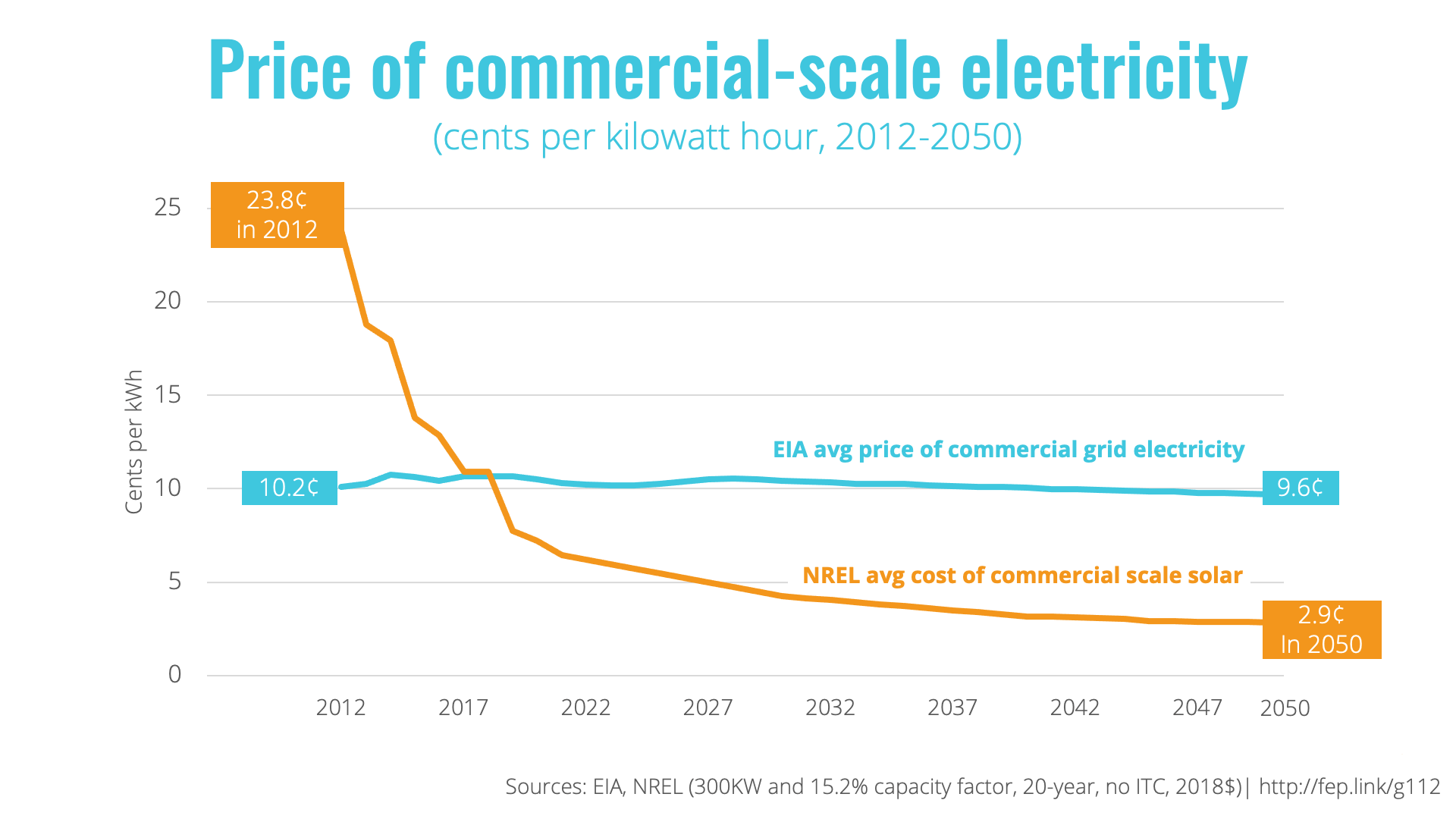
Solar Power Grid Prices
Solar power is increasingly being integrated into electricity grids around the world. As a result, there is a need for transparent and efficient pricing mechanisms to ensure that solar power is fairly compensated and that consumers are not overcharged.There are a variety of different pricing mechanisms used for solar power in various electricity markets.
These mechanisms can be broadly classified into two categories: feed-in tariffs and wholesale market pricing.
Feed-in Tariffs
Feed-in tariffs (FITs) are a type of government subsidy that guarantees solar power generators a fixed price for the electricity they produce. FITs are typically set at a level that is designed to make solar power projects profitable, while also ensuring that consumers do not pay too much for solar power.FITs have been used successfully in a number of countries to promote the development of solar power.
However, they can be expensive for governments to implement and maintain. Additionally, FITs can lead to oversupply of solar power, which can drive down prices and make it difficult for new solar projects to be profitable.
Wholesale Market Pricing
In wholesale market pricing, solar power generators sell their electricity into the wholesale electricity market. The price of solar power in the wholesale market is determined by the supply and demand for electricity.Wholesale market pricing can be more volatile than FITs.
However, it can also be more efficient, as it allows the market to determine the price of solar power based on its value.The choice of pricing mechanism for solar power depends on a number of factors, including the maturity of the solar market, the cost of solar power, and the policy objectives of the government.
Solar Power Grid Incentives
Governments and organizations worldwide have implemented various incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of solar power. These incentives aim to reduce the upfront costs associated with solar power systems and make them more accessible to consumers and businesses.
One of the most common incentives is the solar investment tax credit (ITC), which provides a tax credit for a percentage of the cost of installing a solar power system. Other incentives include rebates, grants, and net metering programs that allow solar power system owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid at retail rates.
Effectiveness of Incentives, Solar power grid prices
The effectiveness of solar power incentives in driving solar power development has been widely debated. Studies have shown that incentives can significantly increase the adoption of solar power, especially in the early stages of market development. However, the impact of incentives can diminish over time as the cost of solar power systems declines and the market matures.
Despite the potential benefits of incentives, it is important to note that they can also lead to market distortions and unintended consequences. For example, incentives can create a dependency on government support and discourage innovation in the solar industry.
Overall, solar power incentives have played a significant role in promoting the adoption of solar power and reducing the cost of solar energy. However, it is important to carefully consider the effectiveness and potential drawbacks of incentives when designing and implementing solar power policies.
Solar Power Grid Challenges: Solar Power Grid Prices
Integrating solar power into the electrical grid presents various technical and operational challenges due to its intermittent and variable nature. These challenges can affect the grid’s stability, reliability, and efficiency.One significant challenge is the variability of solar power generation. Solar power output fluctuates throughout the day and night, and it is also affected by weather conditions.
This variability can make it difficult to predict and balance the grid’s supply and demand.Another challenge is the intermittency of solar power. Solar power is not available at night or during cloudy weather. This can lead to power shortages and grid instability if not properly managed.
Mitigating Challenges
To mitigate these challenges, various strategies can be employed. One strategy is to use energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store excess solar power when it is generated and release it when needed. This helps to smooth out the variability of solar power generation.Another strategy is to use demand response programs, which encourage consumers to shift their energy use to times when solar power is available.
This can help to reduce the demand for electricity during peak hours and make the grid more efficient.Additionally, grid operators can use forecasting tools to predict solar power generation and adjust the grid’s operation accordingly. This helps to ensure that the grid remains stable and reliable even when solar power is variable or intermittent.
Solar Power Grid Future Trends

The future of solar power grid integration is expected to be shaped by several emerging trends and technologies. These include:
- Increased adoption of distributed generation:Distributed generation, such as rooftop solar panels, is becoming increasingly popular as a way to reduce electricity costs and environmental impact.
- Development of new solar technologies:New solar technologies, such as perovskite solar cells and organic photovoltaics, are being developed that are more efficient and less expensive than traditional silicon solar panels.
- Integration of solar power with other renewable energy sources:Solar power is increasingly being integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as wind and hydro power, to create a more reliable and resilient electricity grid.
- Development of new grid technologies:New grid technologies, such as smart grids and microgrids, are being developed to help integrate solar power into the electricity grid more efficiently and reliably.
- Increased government support:Governments around the world are increasingly supporting the development and deployment of solar power, through policies such as feed-in tariffs and tax incentives.
These trends are expected to have a significant impact on the electricity industry. Distributed generation and new solar technologies are likely to lead to a decrease in the cost of electricity, while the integration of solar power with other renewable energy sources and new grid technologies will help to create a more reliable and resilient electricity grid.
Government support is also likely to play a key role in the growth of the solar power industry.
Decentralized Solar Power
One of the most significant trends in solar power grid integration is the increasing adoption of decentralized solar power. Decentralized solar power refers to the generation of solar power at the point of use, such as on rooftops or in small-scale community solar projects.
This trend is being driven by a number of factors, including the falling cost of solar panels, the increasing availability of financing options for solar projects, and the growing demand for renewable energy.Decentralized solar power has a number of advantages over centralized solar power.
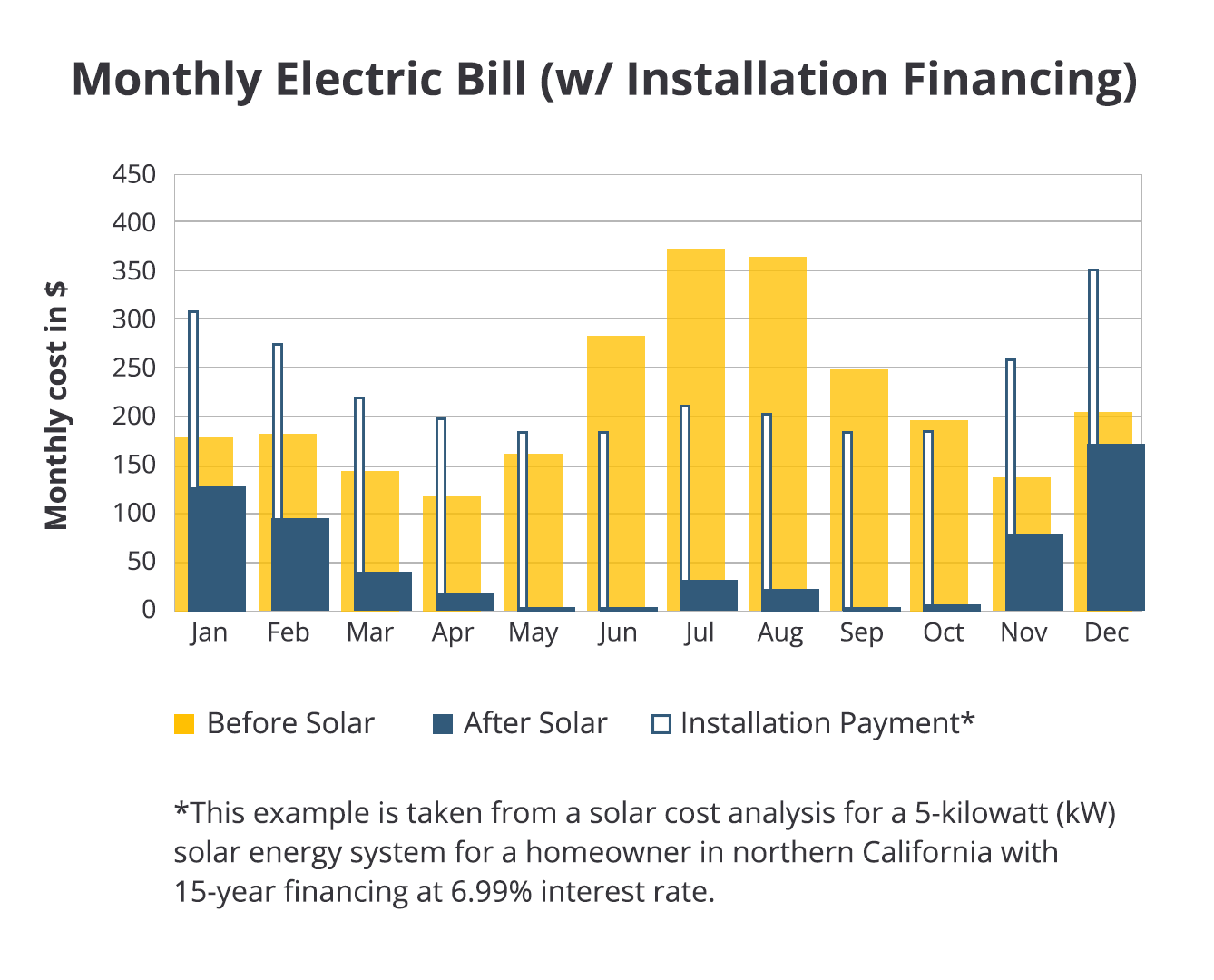
First, it can reduce the cost of electricity for consumers by eliminating the need for transmission and distribution costs. Second, it can help to reduce the environmental impact of electricity generation by reducing the need for fossil fuels. Third, it can help to improve the reliability of the electricity grid by providing a distributed source of power.The adoption of decentralized solar power is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
As the cost of solar panels continues to fall and the availability of financing options for solar projects increases, more and more consumers will be able to afford to install solar panels on their homes or businesses. Additionally, the growing demand for renewable energy is likely to drive the adoption of decentralized solar power, as consumers look for ways to reduce their carbon footprint.
Conclusive Thoughts
As we navigate the future of solar power grid integration, emerging trends and technologies hold immense promise. This exploration concludes with thought-provoking insights into the potential implications of these advancements for the electricity industry, setting the stage for continued innovation and progress in the years to come.
FAQ Overview
What factors influence solar power grid integration costs?
The size and location of the solar installation, the type of grid connection, and the regulatory environment all play a role in determining the costs associated with integrating solar power into the electrical grid.
How do pricing mechanisms impact the profitability of solar power projects?
Pricing mechanisms such as feed-in tariffs, net metering, and wholesale market pricing can significantly affect the financial viability of solar power projects.
What are some common incentives for adopting solar power?
Tax credits, rebates, and performance-based incentives are among the various incentives available to promote the adoption of solar power.
