Blockchain technology, an innovative and revolutionary concept, has emerged as a transformative force in the digital landscape, offering unparalleled levels of security, transparency, and decentralization. Its potential to reshape industries and redefine trust relationships is immense, making it an exciting and rapidly evolving field.
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
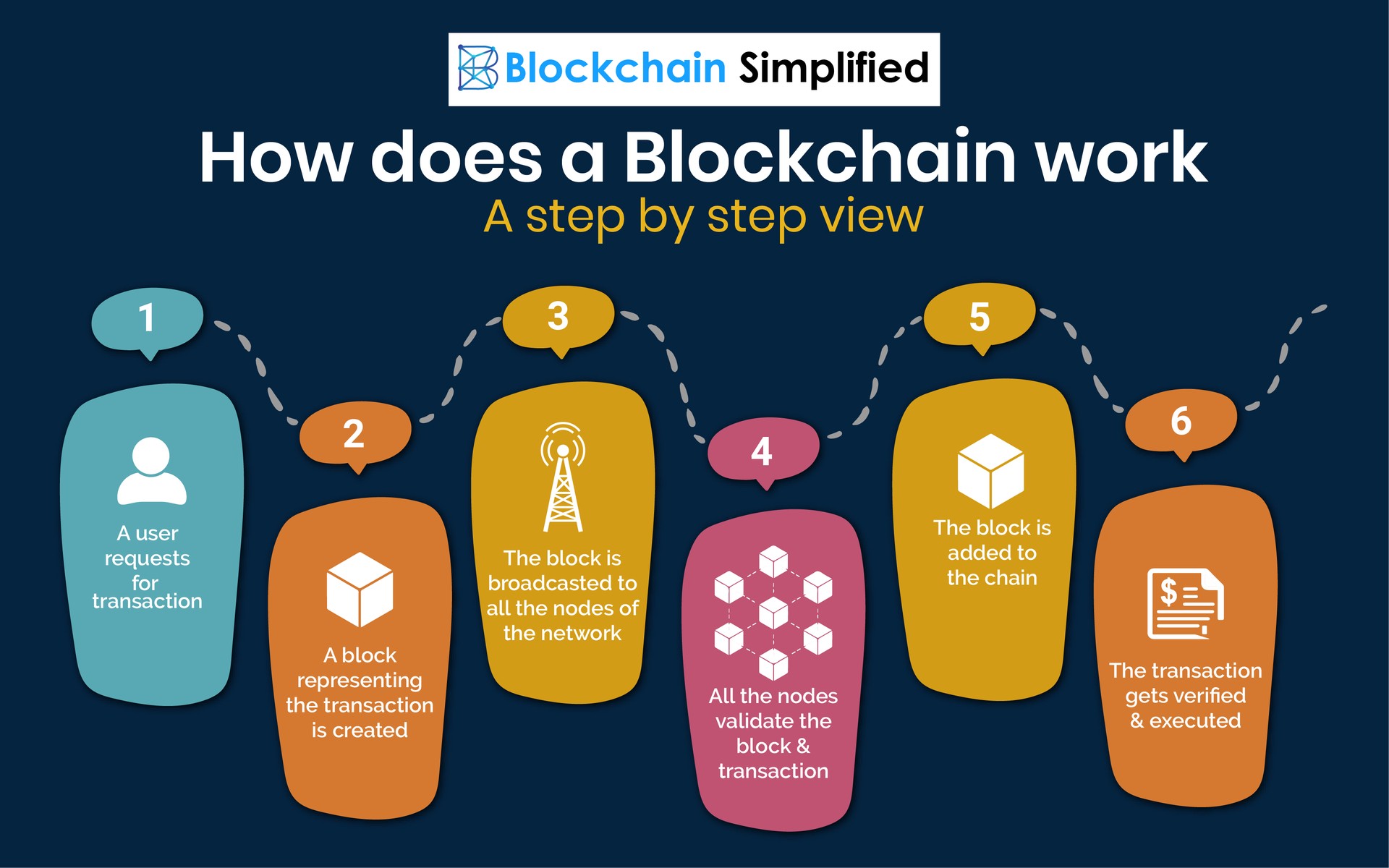
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary new way to store and transfer data. It is a decentralized, distributed ledger that is used to record transactions across many computers. This makes it very difficult to hack or tamper with, as there is no single point of failure.
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize many industries, including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Decentralized and Distributed Nature of Blockchains
One of the key features of blockchain technology is that it is decentralized. This means that it is not controlled by any single entity, such as a bank or government. Instead, it is maintained by a network of computers spread all over the world.
The distributed nature of blockchain technology makes it very difficult to hack or tamper with. If one computer in the network is compromised, the other computers will still be able to maintain the blockchain.
Types of Blockchain Networks: Blockchain Technology

Blockchain networks vary in their accessibility and governance models. They can be classified into three main types: public, private, and hybrid blockchain networks. Each type has distinct characteristics and use cases.
Public Blockchain Networks
Public blockchain networks are open and accessible to anyone. They allow anyone to join the network, participate in consensus, and access the blockchain data. Notable examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Public blockchains prioritize decentralization, transparency, and immutability.
Private Blockchain Networks
Private blockchain networks are permissioned and controlled by a single organization or group of organizations. They offer greater control over who can join the network and participate in consensus. Private blockchains are often used for enterprise applications where data privacy and confidentiality are paramount.
Hybrid Blockchain Networks
Hybrid blockchain networks combine elements of both public and private blockchain networks. They offer a balance between openness and control. Hybrid blockchains can be used for applications that require both public and private components, such as supply chain management or healthcare.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is characterized by several key features that contribute to its transformative potential. These features include immutability, transparency, and security.
Immutabilityrefers to the inability to alter or delete data once it has been added to the blockchain. This is achieved through a consensus mechanism that ensures that all participants in the network agree on the validity of each transaction. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes part of a permanent and tamper-proof record.
Transparencyis another key feature of blockchain technology. All transactions on the blockchain are publicly viewable, providing a level of accountability and traceability that is not possible with traditional systems. This transparency helps to build trust and confidence in the system.
Securityis a critical aspect of blockchain technology. The decentralized nature of the blockchain, combined with cryptographic techniques, makes it extremely resistant to hacking and fraud. Each block in the blockchain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chain of interconnected blocks that is virtually impossible to break.
These key features of blockchain technology enhance trust and reliability in various applications. They provide a secure and transparent way to store and transfer data, making blockchain technology suitable for a wide range of industries and applications.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications across various industries. Some of the most promising use cases include:
Supply Chain Management
- Tracking the movement of goods and materials throughout the supply chain
- Improving transparency and accountability
- Reducing fraud and counterfeiting
Finance
- Facilitating secure and transparent financial transactions
- Reducing the cost of cross-border payments
- Enabling new financial products and services
Healthcare
- Securing and sharing patient medical records
- Improving the efficiency of clinical trials
- Enabling new patient-centric healthcare applications
Government
- Improving the efficiency and transparency of government services
- Reducing corruption and fraud
- Enabling new forms of citizen engagement
Potential Benefits of Blockchain Adoption
- Increased transparency and accountability
- Reduced costs and increased efficiency
- Improved security and privacy
- New opportunities for innovation
Challenges of Blockchain Adoption
- Scalability and performance limitations
- Lack of standardization and interoperability
- Regulatory uncertainty
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, while offering numerous benefits, also faces several challenges and limitations that hinder its widespread adoption. These challenges primarily revolve around scalability, interoperability, and regulatory concerns.
One significant challenge is the scalability of blockchain networks. As the number of users and transactions on a blockchain increases, the network can become congested, leading to slower transaction speeds and higher fees. This scalability issue can limit the practical use of blockchain technology for high-volume applications.
Interoperability
Another challenge lies in the interoperability of different blockchain networks. Currently, various blockchain networks operate independently, making it difficult for them to communicate and exchange data. This lack of interoperability limits the potential for blockchain technology to be used across different applications and industries.
Regulatory Challenges
Regulatory challenges also pose a significant hurdle for blockchain technology. Governments worldwide are still grappling with how to regulate blockchain-based applications and cryptocurrencies. The lack of clear regulatory frameworks can create uncertainty for businesses and hinder the adoption of blockchain technology.
To address these challenges, researchers and developers are actively working on potential solutions. Scalability can be improved through techniques such as sharding, which involves splitting the blockchain into smaller, more manageable segments. Interoperability can be enhanced by developing standardized protocols and bridges that allow different blockchain networks to communicate.
As for regulatory challenges, ongoing discussions and collaborations between governments and industry stakeholders aim to establish clear regulatory frameworks that foster innovation while protecting consumers.
Future Trends in Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries. As the technology continues to mature, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking applications emerge.
One of the most exciting trends in blockchain technology is the development of new consensus mechanisms. Proof-of-Work (PoW), the consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin, is energy-intensive and slow. However, new consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), are more efficient and scalable.
Scalability
One of the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As the number of users and transactions on a blockchain increases, the network can become congested and slow. However, there are a number of promising new technologies that are being developed to address this issue.
- Sharding is a technique that divides a blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces. This can help to improve scalability by reducing the amount of data that each node needs to process.
- Layer-2 solutions are built on top of existing blockchains and can help to improve scalability by handling transactions off-chain. This can free up the main blockchain to process more important transactions.
Interoperability
Another important trend in blockchain technology is the development of interoperability solutions. This will allow different blockchains to communicate with each other and share data. This will make it possible to build more complex and powerful blockchain applications.
Privacy
Privacy is a major concern for many people when it comes to blockchain technology. However, there are a number of new technologies that are being developed to address this issue.
- Zero-knowledge proofs are a cryptographic technique that allows one party to prove to another party that they know a piece of information without revealing the information itself. This can be used to protect the privacy of transactions on a blockchain.
- Confidential transactions are a type of transaction that allows the sender and receiver to remain anonymous. This can be useful for protecting the privacy of sensitive information.
Security
Security is a top priority for blockchain developers. However, there are a number of new threats that are emerging as the technology becomes more popular.
- Quantum computing is a new technology that has the potential to break the encryption that is used to secure blockchains. This could lead to a number of security breaches.
- Social engineering attacks are a type of attack that targets the human element of a blockchain system. These attacks can be used to trick people into giving up their private keys or other sensitive information.
Regulation, Blockchain technology
Regulation is a major challenge for blockchain technology. Governments around the world are still trying to figure out how to regulate this new technology.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has classified some blockchain-based tokens as securities. This means that these tokens must be registered with the SEC before they can be sold to investors.
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has issued guidelines for regulating virtual assets. These guidelines are intended to help governments prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
End of Discussion

As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its applications are expected to expand across various sectors, revolutionizing everything from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and digital identity. Its ability to enhance trust, efficiency, and security holds the promise of a more transparent, secure, and interconnected world.
FAQ Insights
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and tamper-proof manner.
How does blockchain technology work?
Blockchain technology relies on a network of computers to validate and record transactions, creating an immutable and transparent record of all activities.
What are the benefits of blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security, increased transparency, improved efficiency, and reduced costs.
