Internet of Things (IoT) is the seamless integration of physical devices, sensors, and networks that enables the exchange of data and information. This interconnected ecosystem has revolutionized various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing, and continues to shape our future in countless ways.
IoT devices collect and transmit data, providing valuable insights that drive innovation and efficiency. From smart homes to connected cars, IoT is transforming our daily lives and creating a world where technology and the physical realm seamlessly intertwine.
Overview of Internet of Things (IoT)
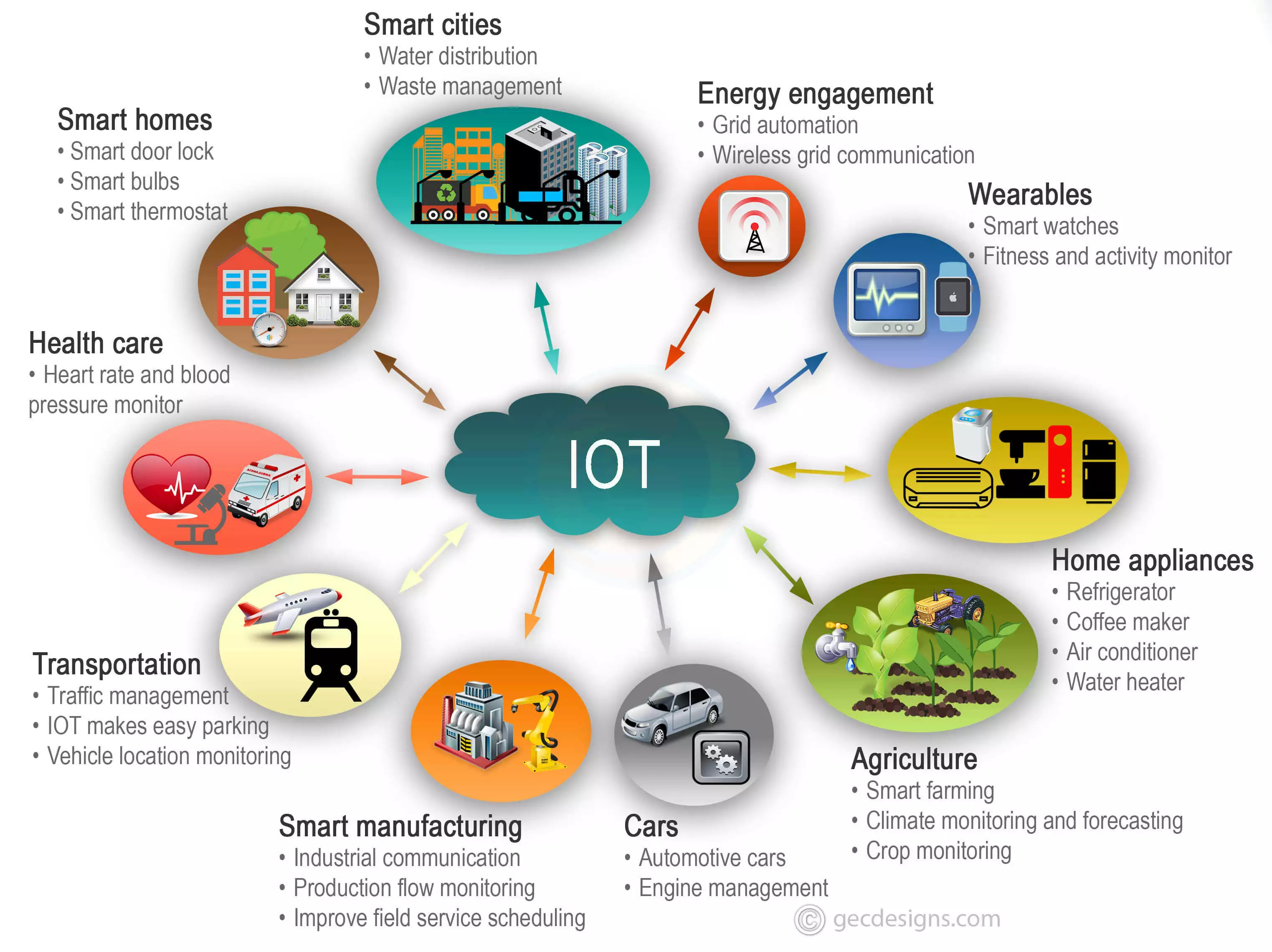
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the growing network of physical devices connected to the internet, enabling them to collect, exchange, and analyze data. These devices, ranging from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, can interact with each other and with external systems, creating a vast and interconnected ecosystem.
A key characteristic of IoT is the ability of these connected devices to communicate with each other and with cloud-based platforms. This allows for the exchange of data, enabling real-time monitoring, remote control, and automated decision-making.
Connected Devices
IoT devices come in various forms, including sensors, actuators, wearables, and smart appliances. These devices are equipped with sensors that can collect data about their surroundings, such as temperature, humidity, motion, and location. Actuators, on the other hand, can perform actions based on received data, such as adjusting lighting, controlling motors, or opening doors.
Data Exchange
The data collected by IoT devices is transmitted over the internet to cloud-based platforms or local servers. These platforms provide storage, processing, and analysis capabilities, enabling users to gain insights from the collected data. The data exchange between devices and platforms is typically facilitated by wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks.
IoT Components and Architecture
An IoT system comprises several components that work together to gather, transmit, and process data from connected devices. These components include sensors, gateways, and cloud platforms.
Sensors are devices that detect and measure physical or environmental parameters, such as temperature, humidity, or motion. They convert these measurements into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to a gateway.
Gateways
Gateways are devices that connect sensors to the cloud platform. They aggregate data from multiple sensors and transmit it to the cloud using wired or wireless communication protocols.
Cloud Platforms
Cloud platforms provide a centralized platform for data storage, processing, and analysis. They also provide tools for device management, data visualization, and application development.
Communication Protocols
IoT networks use various communication protocols to transmit data between devices, gateways, and the cloud platform. These protocols include:
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- Zigbee
- LoRaWAN
- MQTT
The choice of communication protocol depends on factors such as the range, power consumption, and data rate requirements of the IoT application.
Applications and Use Cases of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has far-reaching applications across various industries, transforming the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. IoT devices collect and transmit data, enabling real-time monitoring, automation, and optimization in diverse domains.
Healthcare, Internet of Things (IoT)
- Remote patient monitoring: IoT sensors track vital signs, activity levels, and medication adherence, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and intervene proactively.
- Wearable health devices: Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearables collect health data, providing insights into personal health and well-being.
- Automated drug delivery systems: IoT-enabled devices can dispense medication automatically, ensuring timely and accurate dosing.
Manufacturing
- Predictive maintenance: IoT sensors monitor equipment performance, detecting anomalies and predicting potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Automated production lines: IoT devices control and coordinate production processes, optimizing efficiency and reducing human error.
- Inventory management: IoT sensors track inventory levels in real-time, ensuring optimal stock levels and preventing shortages.
Smart Cities
- Traffic management: IoT sensors monitor traffic flow, optimizing signal timing and reducing congestion.
- Smart lighting: IoT-controlled streetlights adjust brightness based on ambient light levels and occupancy, saving energy and enhancing safety.
- Environmental monitoring: IoT sensors collect data on air quality, noise levels, and other environmental parameters, providing insights for sustainable urban planning.
Benefits and Challenges of IoT Implementation
Benefits:
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced decision-making through data-driven insights
- Improved customer experience and satisfaction
- New revenue streams and business models
Challenges:
- Security and privacy concerns
- Data management and analysis complexity
- Interoperability and standardization issues
- Cost of implementation and maintenance
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of IoT are significant, and organizations across industries are actively exploring and implementing IoT solutions to drive innovation and improve outcomes.
IoT Data Analytics and Security

The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing network of physical devices connected to the internet, collecting and exchanging data. Data analytics plays a vital role in IoT systems, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights from the vast amount of data generated by these devices.
This data can be used to improve operations, optimize processes, and create new products and services.
IoT Data Analytics
- Predictive maintenance:IoT devices can monitor equipment and identify potential problems before they occur, enabling businesses to schedule maintenance proactively and minimize downtime.
- Process optimization:Data analytics can help businesses identify inefficiencies in their processes and optimize them for better performance and cost savings.
- New product development:IoT data can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, helping businesses develop new products and services that meet their needs.
IoT Security
With the increasing number of IoT devices connected to the internet, security risks are becoming a major concern. These devices can be vulnerable to attacks, which can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and even physical harm.
- Malware:IoT devices can be infected with malware that can steal data, control devices, or launch attacks on other systems.
- DDoS attacks:IoT devices can be used to launch DDoS attacks, which can overwhelm websites and online services.
- Phishing:Phishing attacks can trick users into providing their login credentials or other sensitive information.
To mitigate these risks, businesses need to implement robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and firewalls. They also need to regularly update their IoT devices with the latest security patches.
Future Trends and Challenges of IoT
The future of IoT holds exciting prospects, with emerging trends such as artificial intelligence (AI) and edge computing poised to revolutionize the landscape. However, alongside these advancements, challenges must be addressed to ensure the continued growth and success of IoT.
Emerging Trends in IoT
Artificial Intelligence
AI is transforming IoT by enabling devices to learn from data, make predictions, and automate tasks. AI-powered IoT systems can optimize energy consumption, enhance security, and improve decision-making, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the devices that generate it, reducing latency and improving response times. This enables real-time analysis and decision-making, making IoT systems more responsive and effective.
Challenges and Opportunities
Security Concerns
The proliferation of IoT devices creates a vast attack surface, increasing the risk of cyber threats. Robust security measures must be implemented to protect IoT systems from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Data Management
IoT devices generate massive amounts of data, which can be overwhelming to manage and analyze. Efficient data management strategies are crucial to extract valuable insights and ensure data privacy.
Standardization
Lack of standardization across IoT devices and platforms can hinder interoperability and data sharing. Establishing common standards will facilitate the seamless integration and collaboration of IoT systems.
Ethical Considerations
As IoT becomes more pervasive, ethical concerns arise regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential impact on employment. Responsible and ethical practices must be adopted to ensure the responsible and beneficial use of IoT technology.
Concluding Remarks
As IoT continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and data analytics. These technologies will unlock even greater potential for IoT applications, enabling us to harness the power of interconnectedness to solve complex problems, improve our quality of life, and shape a more sustainable and intelligent future.
FAQ Explained: Internet Of Things (IoT)
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
IoT refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, sensors, and software that can collect, exchange, and analyze data.
How does IoT work?
IoT devices use sensors to collect data, which is then transmitted to cloud platforms or other devices for processing and analysis.
What are the benefits of IoT?
IoT offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, cost savings, improved decision-making, and enhanced customer experiences.
What are the challenges of IoT?
IoT implementation can pose challenges related to security, data privacy, and interoperability.
What are the future trends in IoT?
Emerging trends in IoT include the integration of artificial intelligence, edge computing, and blockchain technology.
